3.7 任意定数を含む解をもつ連立 1 次方程式
例 3.31 (任意定数を含む解の具体例)
方程式
を考える. 拡大係数行列の簡約化を行なうと,
を得る. ここで
が成立することに注意する. 簡約化された拡大係数行列より方程式を復元すると,
である. 主成分の列と同じ位置にある変数を左辺に残し, 他の項を右辺に移項すると
となる. 右辺にある変数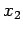 ,
, 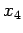 は独立に任意の値をとる.
よって
は独立に任意の値をとる.
よって
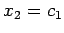 ,
,
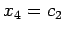 とおけば,解として
とおけば,解として
を得る. 解は 5 次元平面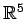 内の
ある 2 次元平面となる.
内の
ある 2 次元平面となる.
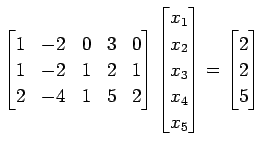 |
(450) |
を考える. 拡大係数行列の簡約化を行なうと,
![$\displaystyle \left[\begin{array}{ccccc\vert c} 1 & -2 & 0 & 3 & 0 & 2 \\ 1 & -...
... & 0 & 2 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & -1 & 0 & -1 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 1 \end{array}\right]$](img935.png) |
(451) |
を得る. ここで
| (452) |
が成立することに注意する. 簡約化された拡大係数行列より方程式を復元すると,
![$\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{cccccl} x_{1} & -2x_{2} & & +3x_{4} & & = 2 ...
...m] & & x_{3} & -x_{4} & & = -1 \\ [.5em] & & & & x_{5} & = 1 \end{array}\right.$](img937.png) |
(453) |
である. 主成分の列と同じ位置にある変数を左辺に残し, 他の項を右辺に移項すると
![$\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{cl} x_{1} & = 2 + 2x_{2} - 3x_{4} \\ [.5em] x_{3} & = -1 +x_{4} \\ [.5em] x_{5} & = 1 \end{array}\right.$](img938.png) |
(454) |
となる. 右辺にある変数
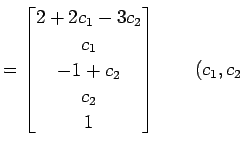 :任意定数 :任意定数 |
(455) | |
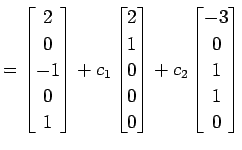 |
(456) |
を得る. 解は 5 次元平面
Kondo Koichi

平成17年9月15日